Cell CycleCheckpoint Biology Diagrams Learn about cell cycle checkpoints and their role in regulating the cell cycle. Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that results in cell growth and division. Find out the phases, regulators, and checkpoints of the cell cycle with diagrams and examples.
Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. These checkpoints include: G 1 Checkpoint: This checkpoint ensures that the cell has adequate energy resources and that the surrounding environment is favorable for DNA replication. If conditions aren't right, the cell can exit to G 0 phase. G 2 Checkpoint: Before entering mitosis

Cell Cycle: Stages of Cell Cycle, Checkpoints, Diagram Biology Diagrams
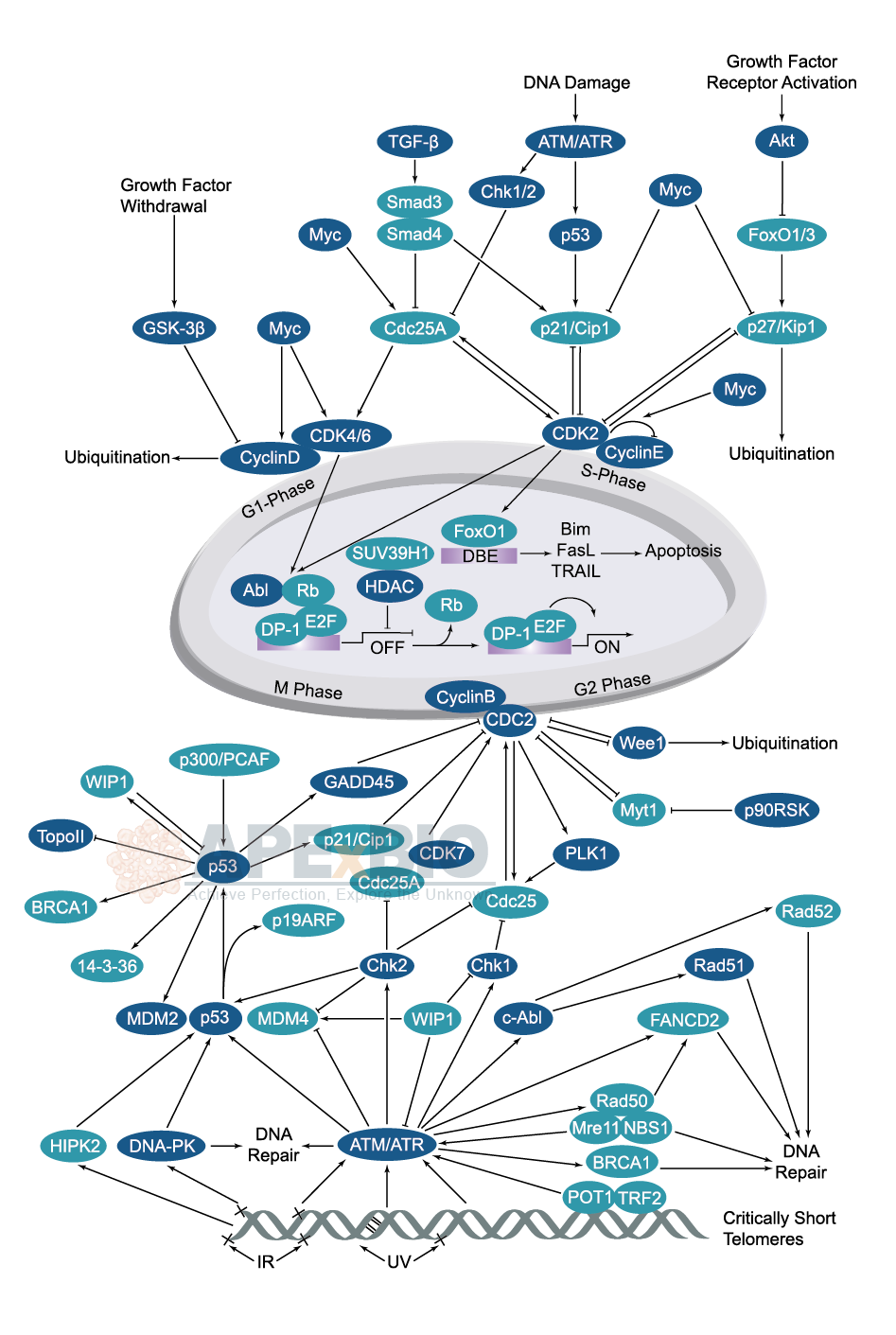
To prevent a compromised cell from continuing to divide, there are internal control mechanisms that operate at three main cell cycle checkpoints at which the cell cycle can be stopped until conditions are favorable. These checkpoints occur near the end of G 1, at the G 2 -M transition, and during metaphase (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)).

Visual Representation of the Cell Cycle Diagrams and Figures. Figure 9.15: Illustrates the checkpoints in the cell cycle, highlighting the G₁, G₂, and M phases as critical control points. Figure 9.16: Depicts the G₀ phase and its significance in the life cycle of cells, particularly in mature tissues.

7.4: Cell Cycle Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. See the diagram of the cell cycle phases, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis, and the regulatory checkpoints that control the process.
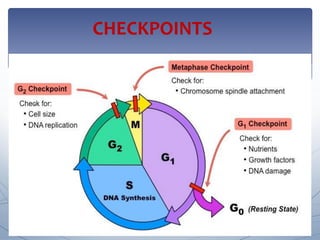
The cell cycle includes several checkpoints, where the major ones are the G 1, G 2 and M checkpoint. G 1 checkpoint - size and nutrient verification. This checkpoint, also called the restriction checkpoint, takes place between the G 1 and the S phase. The cell verifies that it is large enough to divide, that its DNA is intact, and if there is

