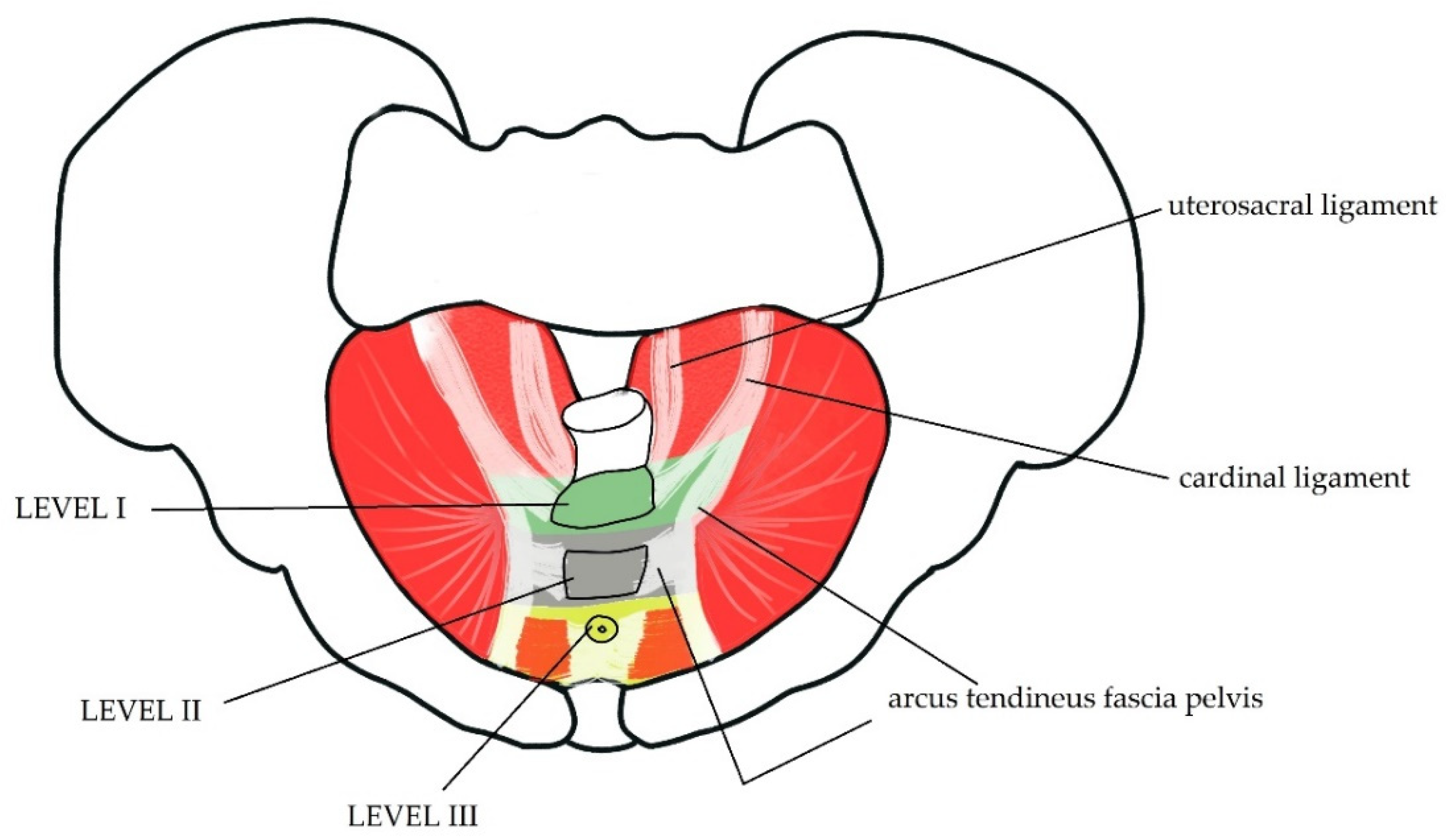
Pelvic Floor Physio Brisbane Biology Diagrams Learn about the anatomy and functions of the pelvic floor, a funnel-shaped structure that supports the pelvic viscera and maintains urinary and faecal continence. The pelvic floor consists of three main components: levator ani, coccygeus and fascia coverings.

INTRODUCTION. Pelvic floor muscles have two major functions; they provide 1; support or act as a " floor" for the abdominal viscera including the rectum and 2; constrictor or continence mechanism to the urethral, anal and vaginal orifices (in females).Here, we will discuss the relevance of pelvic floor to the anal opening and closure function, and discuss new findings with regards to the
The Pelvic Floor Biology Diagrams
The pelvic floor is a unique anatomical location where the balance of the different pressures, either visceral, muscular, or liquid play a fundamental role in the physiological functioning of all the structures contained therein. The pelvis is bounded superiorly by the imaginary line between the pubis and sacral promontory and inferiorly as the line between the ischial tuberosity and the apex

Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women: a cochrane systematic review abridged republication. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 54(3), 416-432. ↑ Sapsford, R. (2001). Rehabilitation of pelvic floor muscles utilizing trunk stabilization.

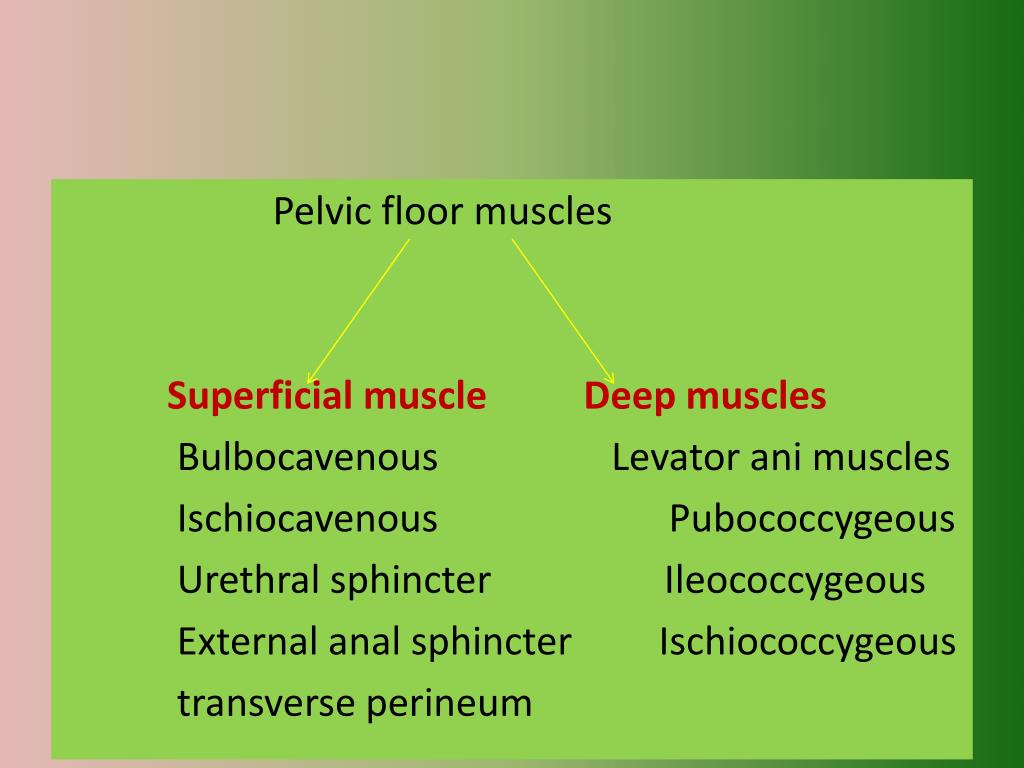
Muscles of the Pelvis Biology Diagrams
Pelvic floor dysfunction refers to a set of indications and symptoms caused by faulty pelvic floor muscle activity. The pelvic floor muscles in women support the urethra, vagina, and anal canal. Weakness of these muscles can lead to a lack of structural support for these organs, manifesting as: