Shoulder Muscles Part 3 The Rotator Cuff Biology Diagrams Learn about the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, a group of tendons that stabilize and move your shoulder joint. Find out the common injuries, symptoms, and treatments of rotator cuff problems.
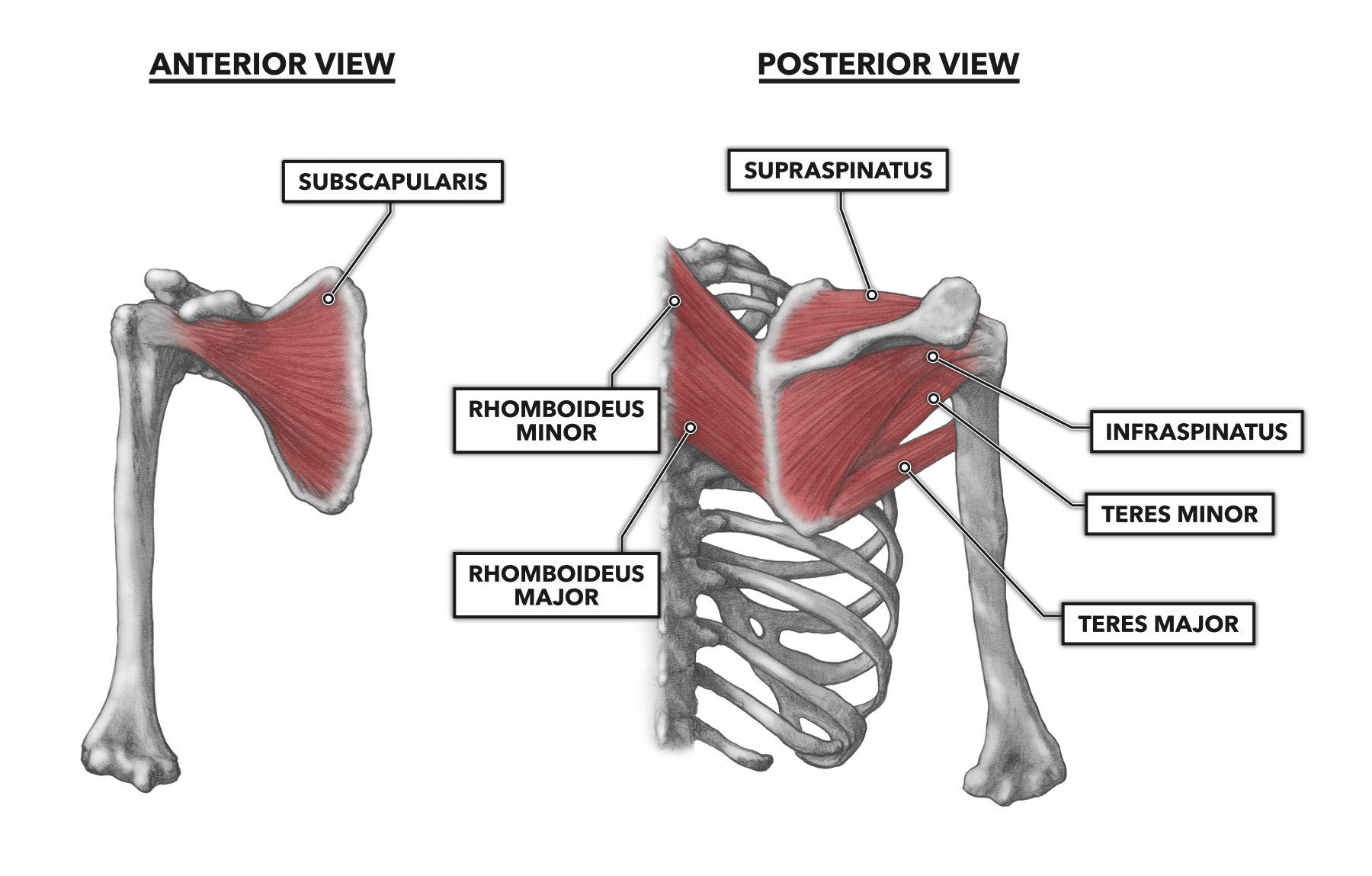
Learn about the four muscles of the rotator cuff, their origins, insertions, innervations and roles in shoulder movements and stability. Find out the common pathologies and clinical aspects of the rotator cuff, such as impingement syndrome and tears. The rotator cuff (SITS muscles) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are: supraspinatus muscle; infraspinatus muscle; teres minor muscle;

Rotator Cuff: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment Biology Diagrams
Learn about the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that surrounds your shoulder joint and helps you move and stabilize your arm. Find out the common causes, symptoms and treatments of rotator cuff injuries.
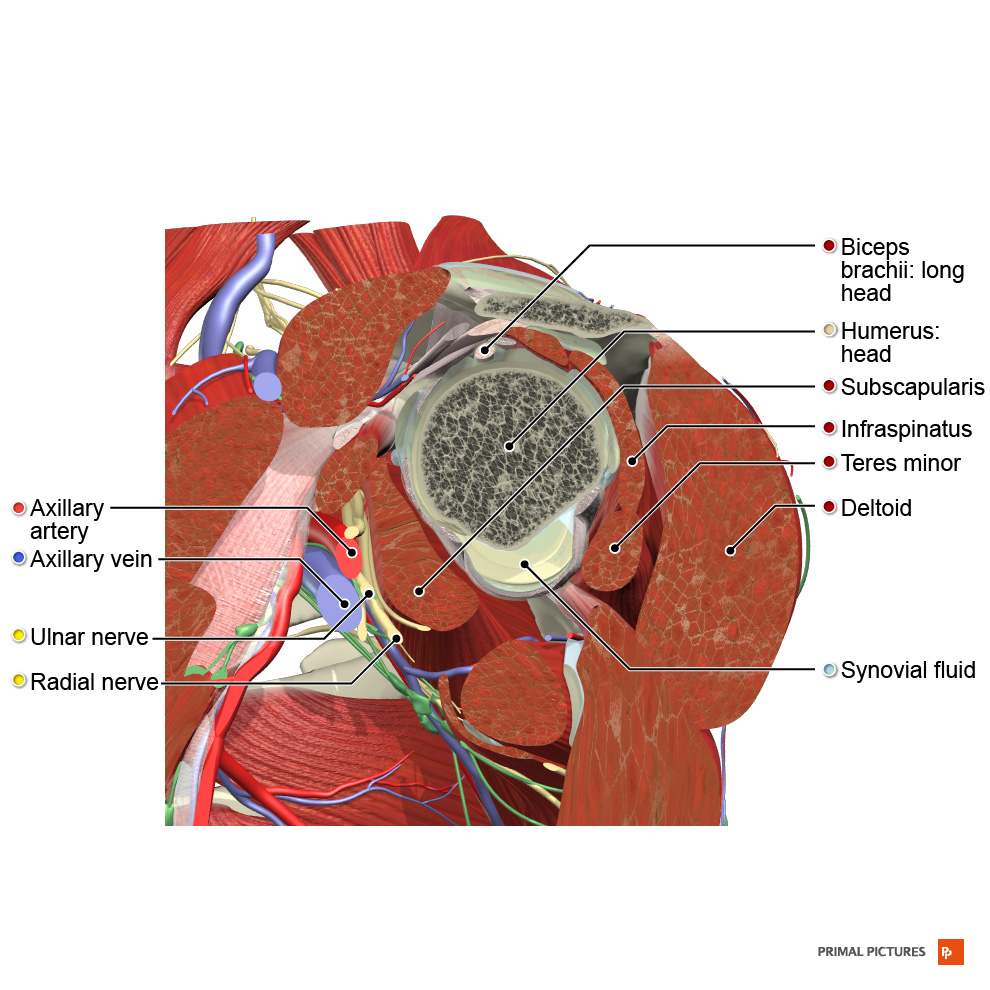
Learn about the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, their roles in shoulder stability and movement, and how they can get injured. Find out the common causes, symptoms, and treatments of rotator cuff problems.

Structure and function of the rotator cuff Biology Diagrams
The Rotator Cuff (RC) is a common name for the group of 4 distinct muscles and their tendons, which provide strength and stability during motion to the shoulder complex. They are also referred to as the SITS muscle, with reference to the first letter of their names ( Supraspinatus , Infraspinatus , Teres minor , and Subscapularis , respectively).

